RelevanceCore Settings
Relevance optimizes how well the search results match the user’s intent and query. Increasing relevance means happier users through better findability of products and documents.
Relevant search results are important for:
-
E-commerce sites, where relevant results drive conversions and revenue.
-
Support sections of sites, such as help pages, where relevance reduces customer frustration and complaints.
-
Enterprise search, where relevance boosts productivity and knowledge discovery by helping employees find what they need to perform their work or solve a problem.
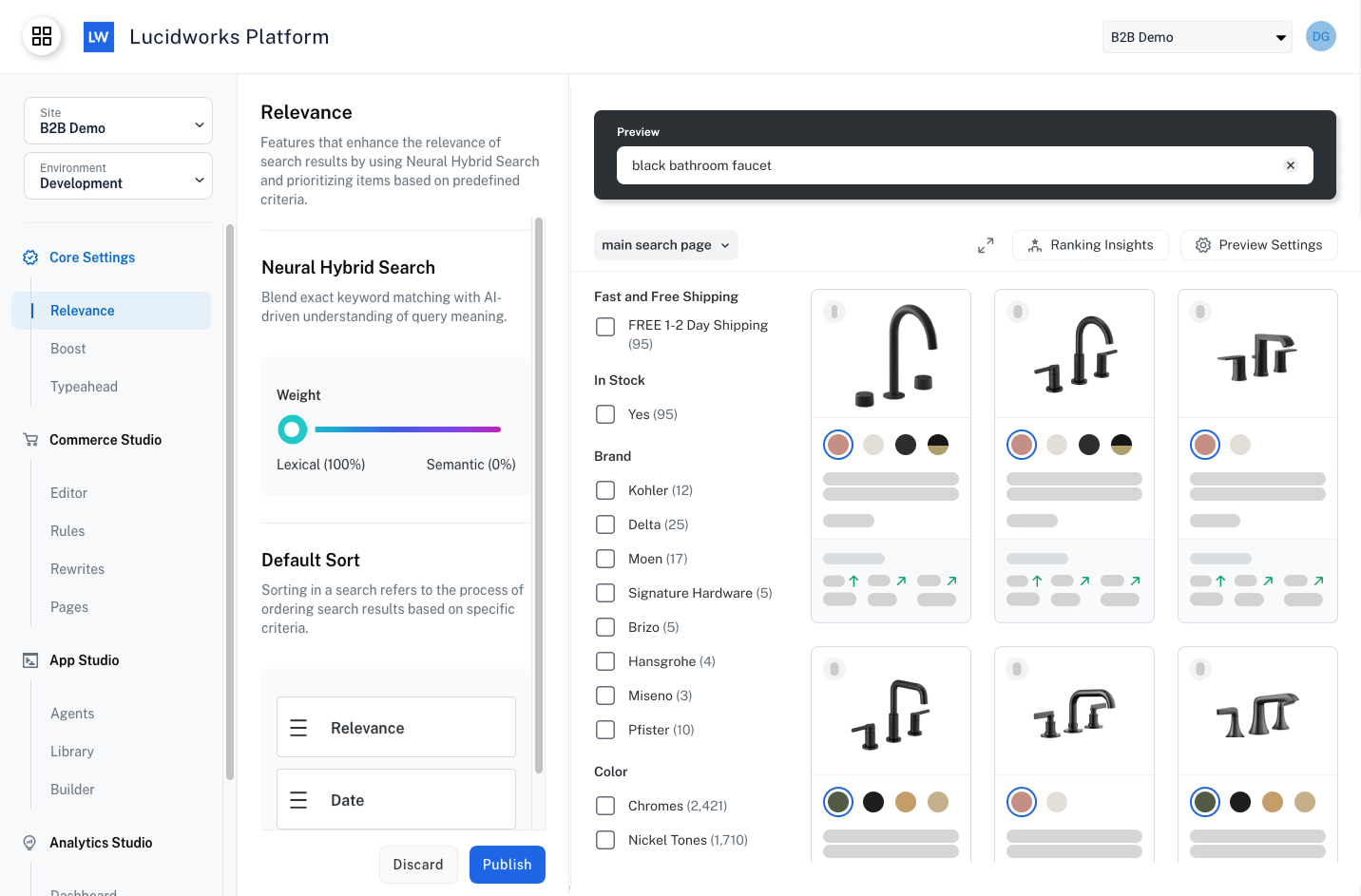
Neural Hybrid Search
Lucidworks Core Settings includes the option of using Neural Hybrid Search (NHS) to take advantage of advanced searching capabilities that combine lexical search and semantic search, enabling exact and partial keyword matching, phrase detection, and search results that understand the natural language users might enter in the search box.
Lexical search is the basic type of search that uses exact matching of keywords to return results. It is useful for situations where the results are simple and predictable, or when a keyword always returns what the user is trying to find. Lexical search can be a good solution for smaller datasets that are well-organized but struggles when the wording of the query is not exact or with common keywords.
Semantic search understands the meaning behind the words used in a query and can compare the relationship of the query to the conceptual representation of items in a dataset to return more relevant results. With semantic search, exact keyword matches are not needed, giving the user more freedom in how they word their searches. An additional benefit of semantic search is the ability to return related results, even if those results do not include the keyword entered by the user.
NHS uses both of these to optimize the search experience.
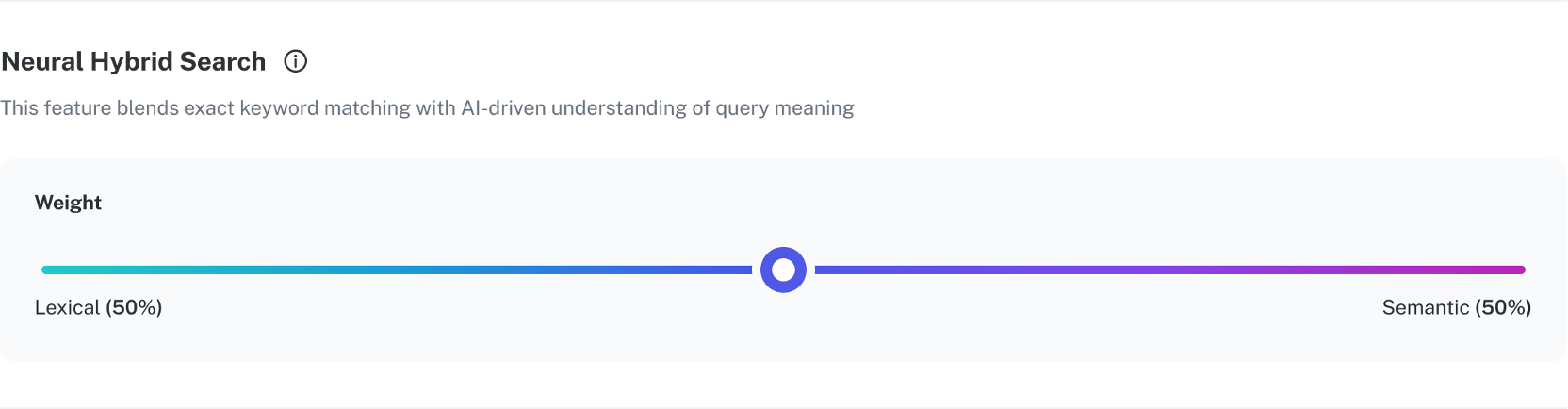
Use the slider to decide the relative importance of lexical and semantic search for your search results. As you increase the weighting of one type of search, the other type of search decreases.
Depending on the type of content you have, you can adjust the slider to accommodate the information you want the user to see. For example, a legal, medical, or financial website might have industry-specific words that benefit from a more lexical approach, while an e-commerce website might want to show users similar products and will benefit from giving a greater weighting to semantic search.
Fine tune the results
Evaluate the specific needs of your use case to determine the appropriate balance between lexical and semantic search.
Begin testing by starting in the middle with 50% lexical and 50% semantic and perform a series of queries. If the results do not match your expectations, then adjust the slider.
In a B2C context such as a grocery store chain, if a user searches for "ice cream" and the results prioritize "bag of ice" and "sour cream," the semantic weight should be increased. This helps return contextually relevant items like "waffle cones" and "chocolate syrup" that align with the shopper’s intent.
In contrast, on a financial services site where a user is researching "bonds," overly broad results like CDs, mutual funds, or ETFs may dilute relevance. Increasing the lexical weight ensures the top results remain focused on bonds.
Adjust the weighting strategy to match user intent and the goals of your business.
Adjust the weights for your specific use case, and validate that the search results become more relevant for the users.
Sort
Sort is how search results are ordered and can be set according to relevance, which is the degree to which each item matches a user’s query based on search settings.
You can change the default sorting order that is used for results by arranging the tiles in the Sort section. This lets you sort first by relevance, then by date for items with identical relevance, or sort first by date, then by relevance for items with identical dates.