Indexing Data Flow
With Fusion, your data is indexed in a set of collections in Fusion’s Solr core.
A primary collection holds your searchable content, such as your product catalog, knowledge base, blog articles, product reviews, and so on.
A set of secondary collections are associated with your primary collection to hold related data that Fusion can use to enhance the relevancy of your search results.
This topic shows you how different types of data flow through Fusion to be indexed in your primary and secondary collections.
1. Index your content
No matter where your content is located, Fusion can index it. The Fusion collection where your searchable content is indexed is called the primary collection. Secondary collections are automatically created to hold related data, such as signals, machine learning job output, and so on.
There are a few ways to index your searchable content to the primary collection:
-
Lucidworks has a wide variety of connectors for many types of data sources. Find your connector.
Once the connector fetches your data, parsers read it before passing it to the index pipeline.
-
The gRpc remote framework is configured on the client side and only works with V2 type connectors.
-
V1 classic connectors support ingesting data using IP white lists, VPN tunnels, and public channels.
-
-
The Parallel Bulk Loader (PBL)
The PBL can send your data to an index pipeline or directly to the primary collection, depending on whether the data requires transformation before indexing. It does not support parsers and is not recommended for production environments.
-
Send your content to an index profile using the Fusion REST API. Index profiles are saved configurations of parsers and index pipelines.
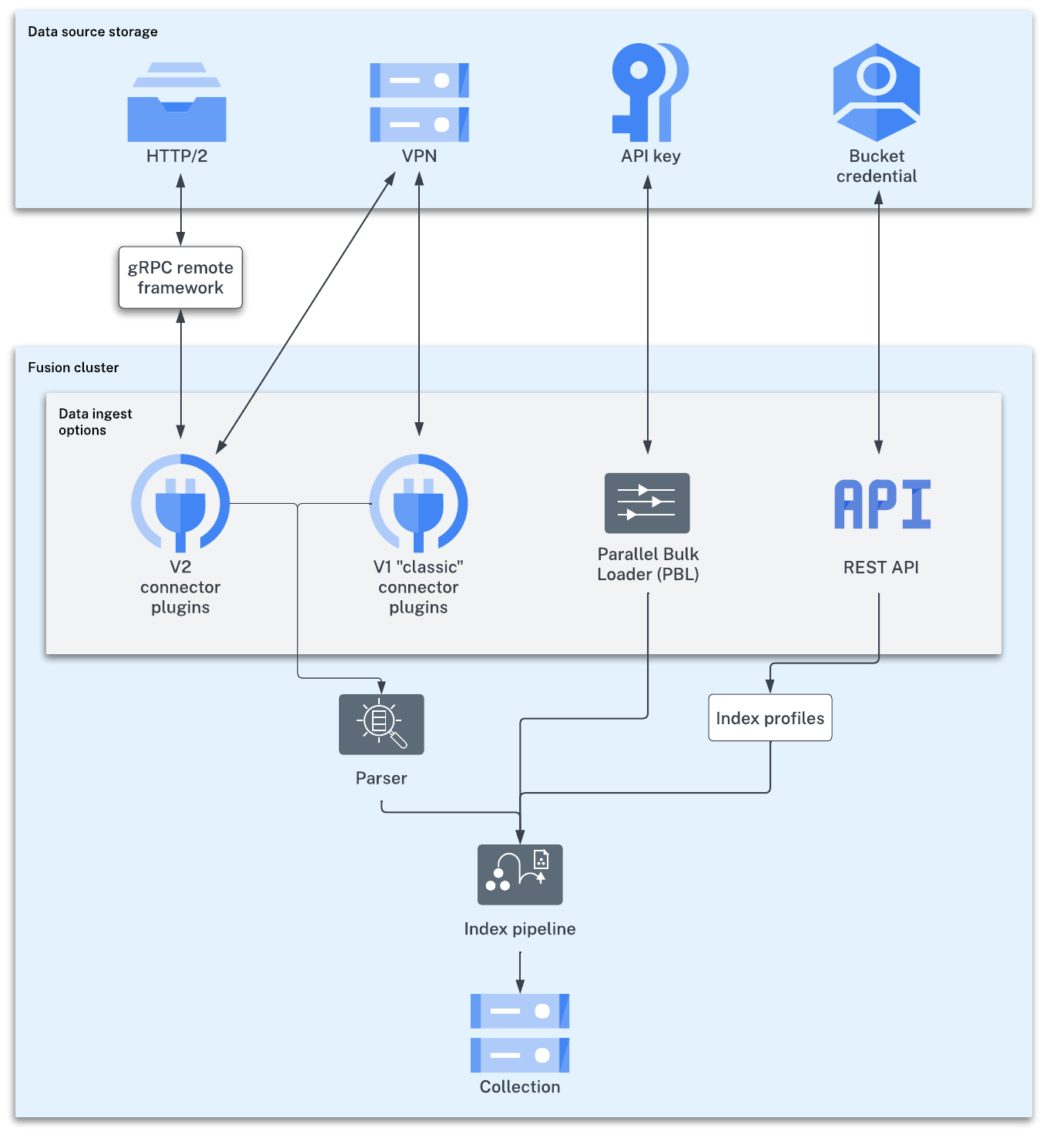
The index pipeline consists of one or more configurable index pipeline stages, each performing a different type of transformation on the incoming data. Each connector has a default index pipeline, but you can modify these or create new ones.
The last stage in any index pipeline should be the Solr Indexer stage, which submits the documents to Solr for indexing.
2. Index your signals
Signals are event records that provide historical data about user behavior, such as clicks, likes, purchases, and so on. You don’t need to index signals about query responses; Fusion indexes response signals automatically by default. If you are using App Studio or App Insights, then you need to index request signals. Learn more about signal types and required fields.
To index your signals, you send them to Fusion using the Signals API, which points to the hidden index pipeline designed especially for signals.
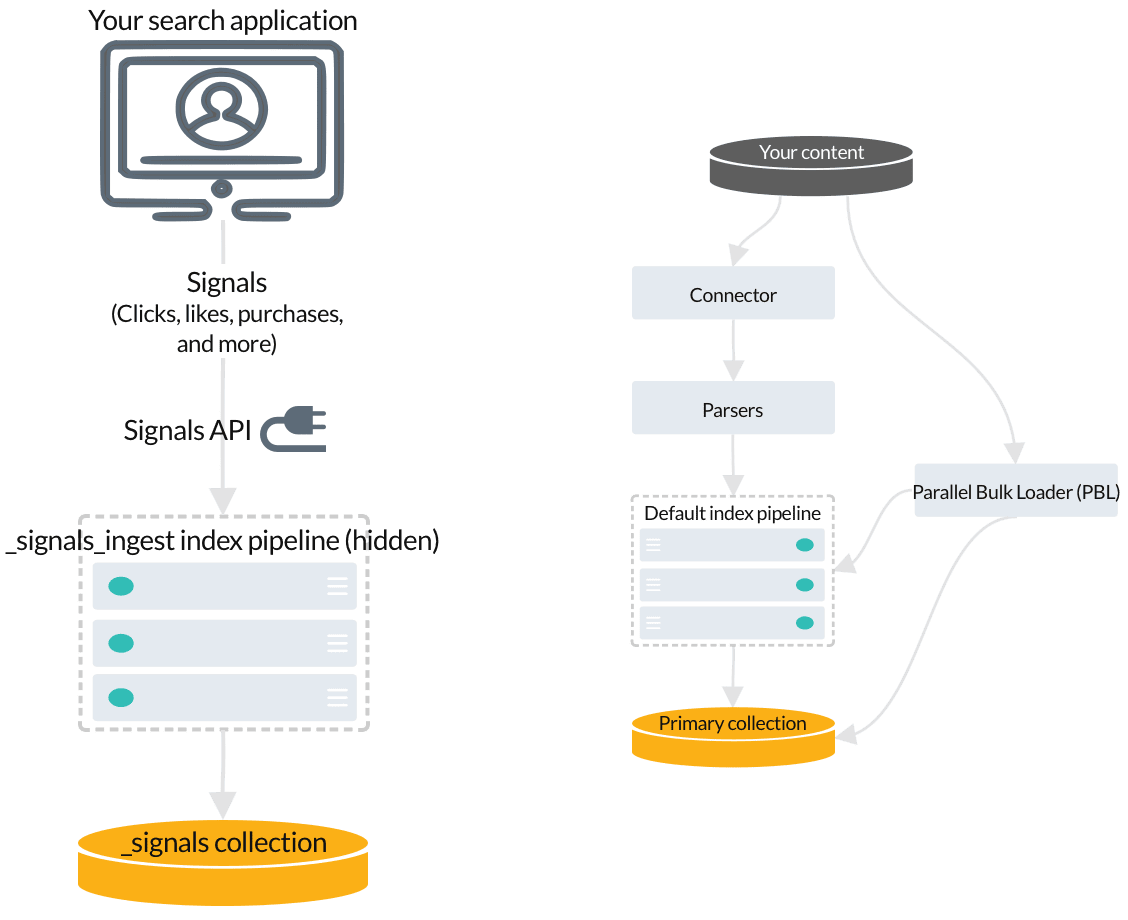
Raw signals are indexed in a secondary collection called COLLECTION_NAME_signals. For example, if your primary collection is called Products, then the raw signals collection is Products_signals.
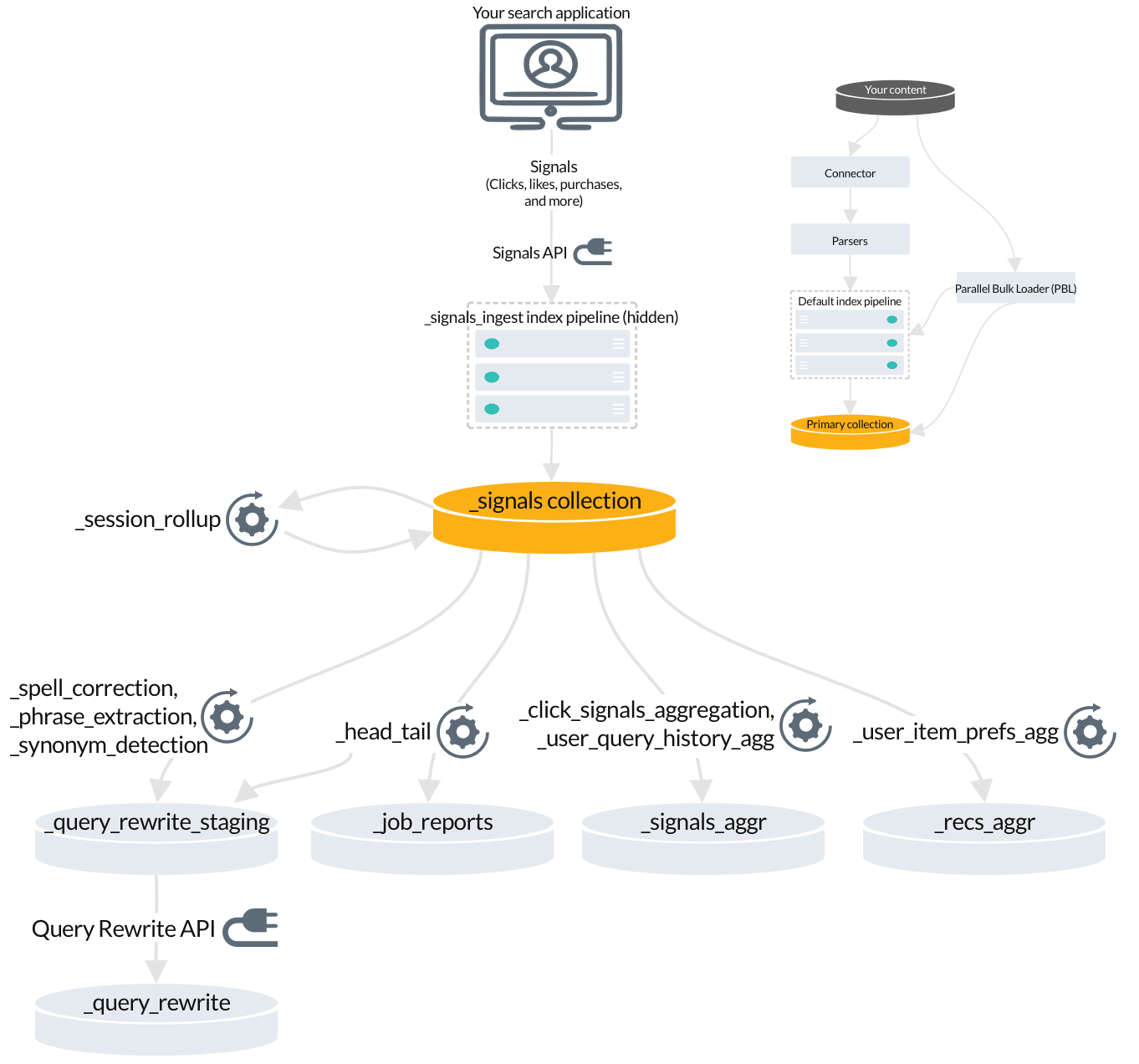
3. Fusion jobs that index signals-related data
When you enable signals, Fusion creates jobs and secondary collections for analyzing and aggregating your raw signals. Some of this data enables query rewriting and automatic boosting, while other data becomes useful when you enable recommendations.
-
The
_session_rollupjob creates session signals from your raw signals and adds them to the_signalscollection. -
Automatic query rewrites are created by several jobs and indexed in the
_query_rewrite_stagingcollection for review before they are published to the_query_rewritecollection. -
The
_head_tailjob sends rewrites for underperforming queries to the_query_rewrite_stagingcollection. It also sends analytics tables to the_job_reportscollection. -
The
_signals_aggrcollection stores unique combinations of query, document ID, and filters found in your raw signals, each with a timestamp, weight, and count. These are generated by the_click_signals_aggregationjob and the_user_query_history_aggjob. -
The
user_item_prefs_aggjob identifies unique pairs of document IDs and user IDs, assigns a timestamp, weight, and count to each pair, and indexes it in the_recs_aggrcollection.
4. Fusion jobs that index recommendations
When you enable recommendations, another set of jobs and secondary collections is created.
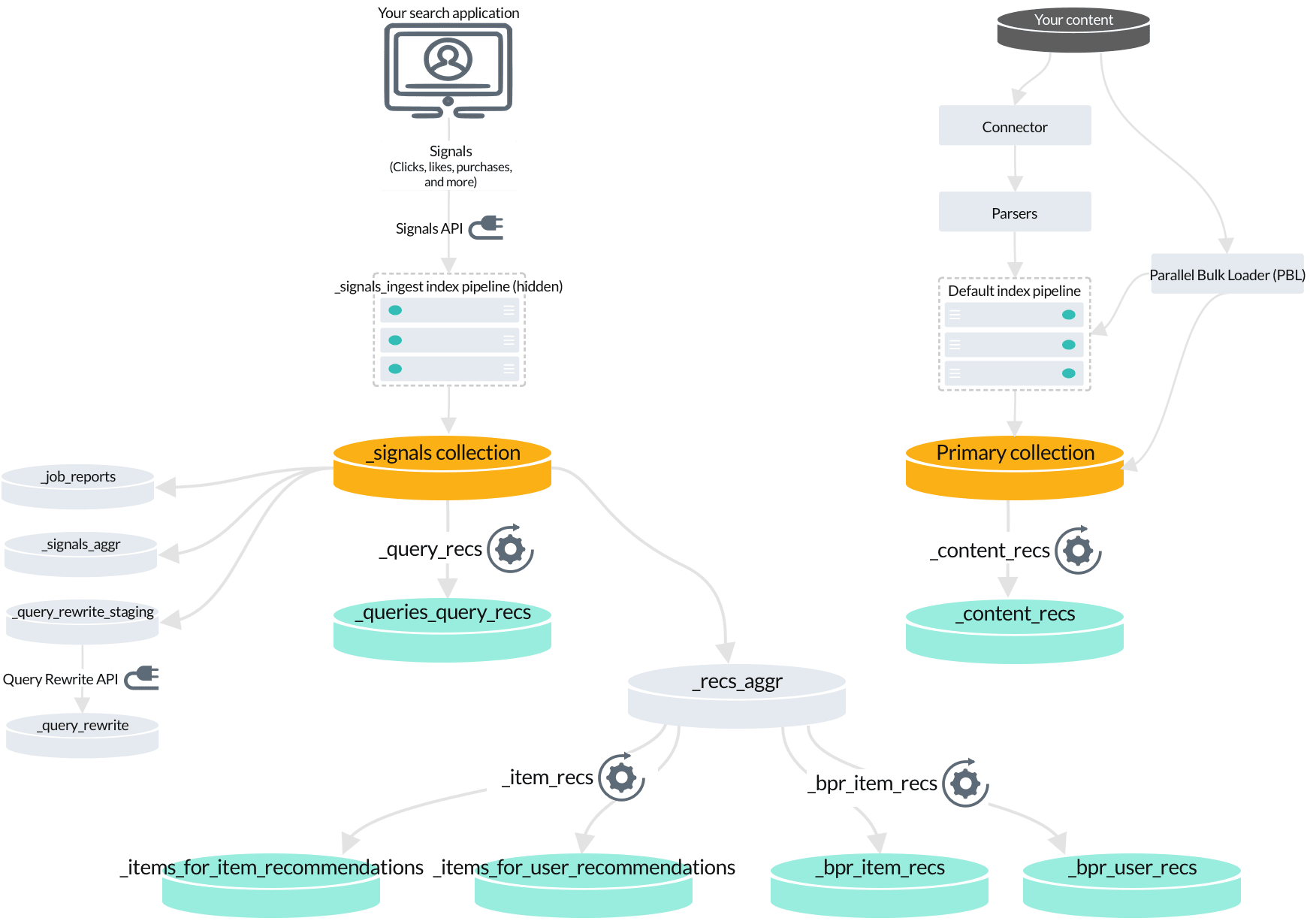
The default recommendation jobs read data from different collections depending on the type of recommendations being generated:
-
Content-based recommendations are produced by the
_content_recsjob by analyzing your primary collection. -
Queries-for-query recommendations are produced by the
_query_recsjob by analyzing your raw signals. -
BPR-based items-for-item and items-for-user recommendations are produced by the
_bpr_item_recsjob by analyzing aggregated signals.
| For more recommendations, try configuring the Trending Recommender job. |
What’s next?
See Query Data Flow to learn about querying your content and recommendations.