Index DataGetting Started with Managed Fusion
This topic details how to configure a datasource using Index Workbench.
General information
Managed Fusion’s Index Workbench provides the tools to configure datasources, parsers, and index pipelines. It lets you preview the results of indexing before you load your data into the actual index.
When you enter the necessary data extraction configuration in Index Workbench, it retrieves a small number of documents as sample data.
Since this processing is simulated, and actual data is not yet ingested, you can preview the sample documents to test and refine the index pipeline before all of the data is loaded into the actual index.
When you complete and save the configuration, it is saved in Index Workbench as a Managed Fusion datasource. To load your data into Managed Fusion, use the Datasource tool to run the resulting configuration.
Before you begin
To perform the steps in this part of the tutorial, you must complete Part 1 - Create a Managed Fusion application.
| Throughout these tutorials, it is important to save your work regularly. The steps include instructions to save, but you can save your work more frequently if needed. When you configure datasources, pipelines, and other settings on your own site, saving your changes regularly is essential. |
Download the MovieLens dataset
-
This is a MovieLens dataset created by the Grouplens research lab.
-
Unpack the
ml-latest-small.zipfile.Managed Fusion can parse
.zipfiles, but in this tutorial, we will index just one file from the archive (movies.csv).The
movies.csvfile contains a list of 9,125 movie titles, plus a header row. Here is a truncated listing:movieId,title,genres 1,Toy Story (1995),Adventure|Animation|Children|Comedy|Fantasy 2,Jumanji (1995),Adventure|Children|Fantasy 3,Grumpier Old Men (1995),Comedy|Romance 4,Waiting to Exhale (1995),Comedy|Drama|Romance 5,Father of the Bride Part II (1995),Comedy 6,Heat (1995),Action|Crime|Thriller 7,Sabrina (1995),Comedy|Romance 8,Tom and Huck (1995),Adventure|Children 9,Sudden Death (1995),Action 10,GoldenEye (1995),Action|Adventure|Thriller
Open the Movie Search app
-
Sign in to Managed Fusion if it is not currently open.
-
In the Managed Fusion launcher, click the Movie Search app.
-
To verify the Movie Search app is selected to display in the workspace:
-
Hover over Apps
 . Movie Search is the currently selected app.
. Movie Search is the currently selected app. -
Review the collection picker selection at the top of the screen.
Movie_Searchis selected as the default collection for the Movie Search app, and is where Managed Fusion will place index data.
-
Configure the datasource
A collection includes one or more datasources. A datasource is a configuration that manages the import, parsing, and indexing of data into a collection.
-
Click Indexing
 > Index Workbench.
> Index Workbench. -
Click New.
-
In the Add A New Datasource section, click Or, upload a file.
-
Click Choose File.
-
Navigate to the
movies.csvfile on your computer, select it, and click Open. The file name displays on the screen.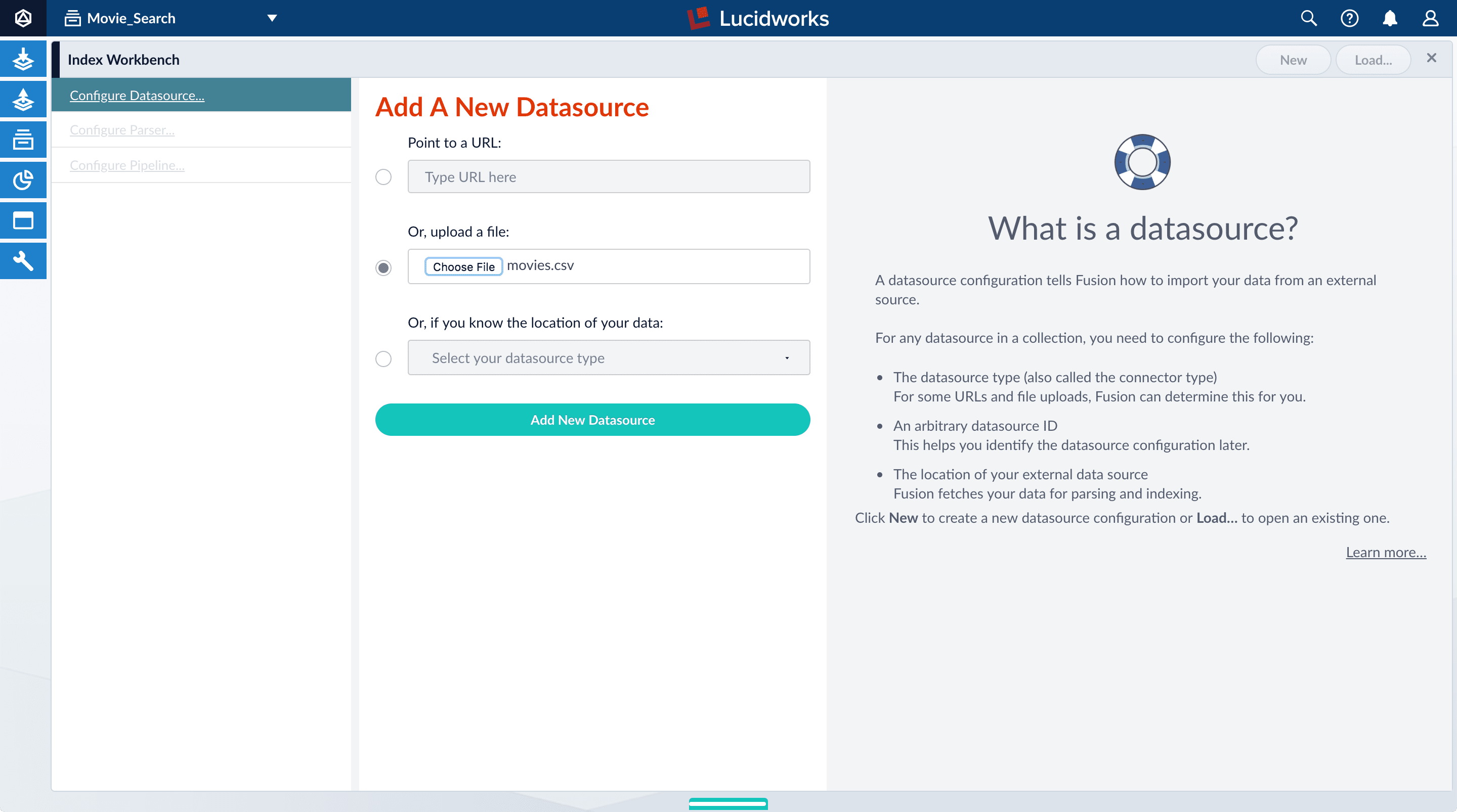
-
Click Add New Datasource.
The Datasource (File Upload) configuration panel displays the default datasource ID
movies_csv-Movie_Searchand the default file IDmovies.csv. You do not have to change these values. -
Enter the Description
Movies CSV file.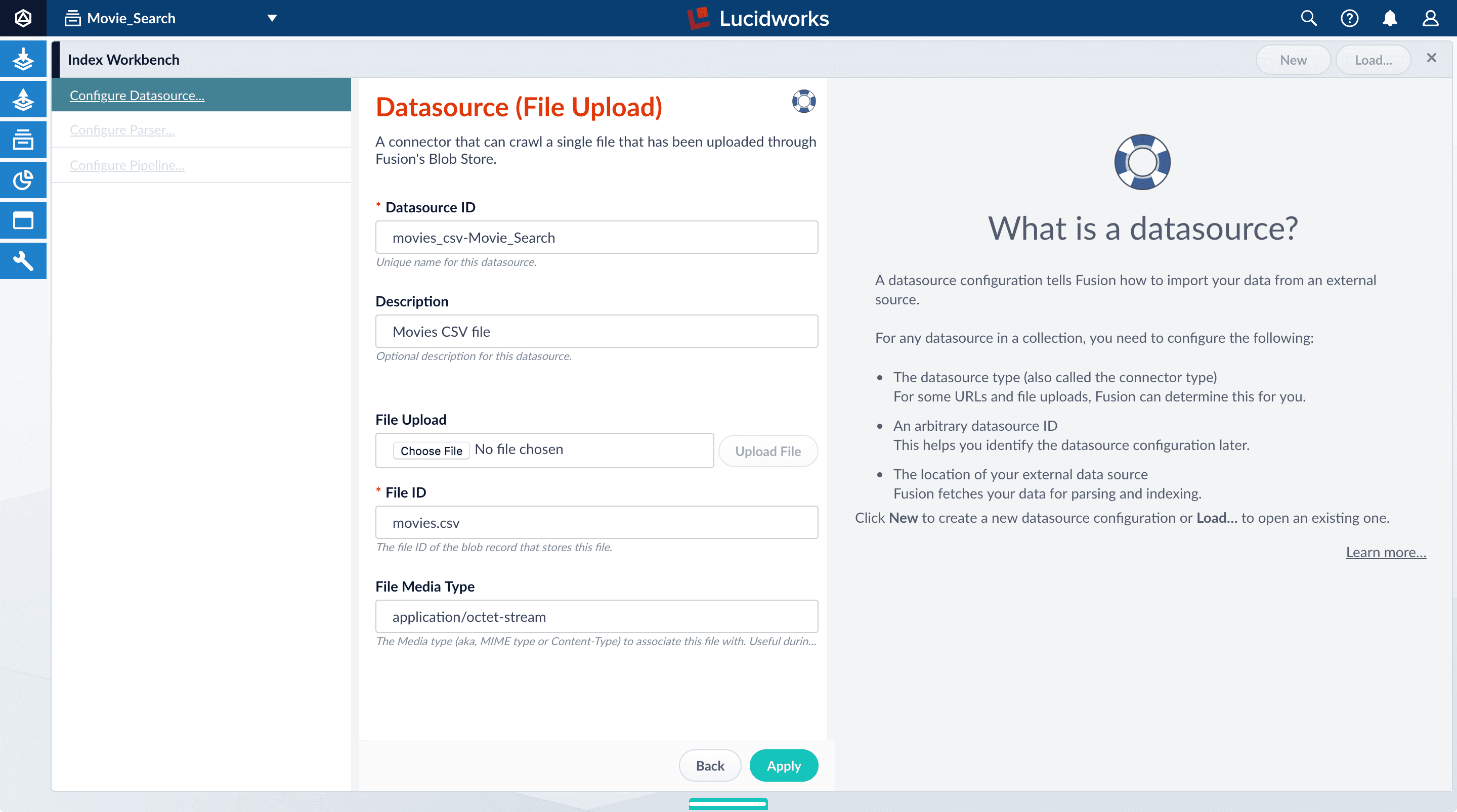
-
Click Apply.
Index Workbench reads up to 20 documents into memory from the
movies.csvfile, and then displays a preview of how they would be indexed based on current parameter and field settings.You have finished configuring the datasource. At the bottom of the page, click Cancel.
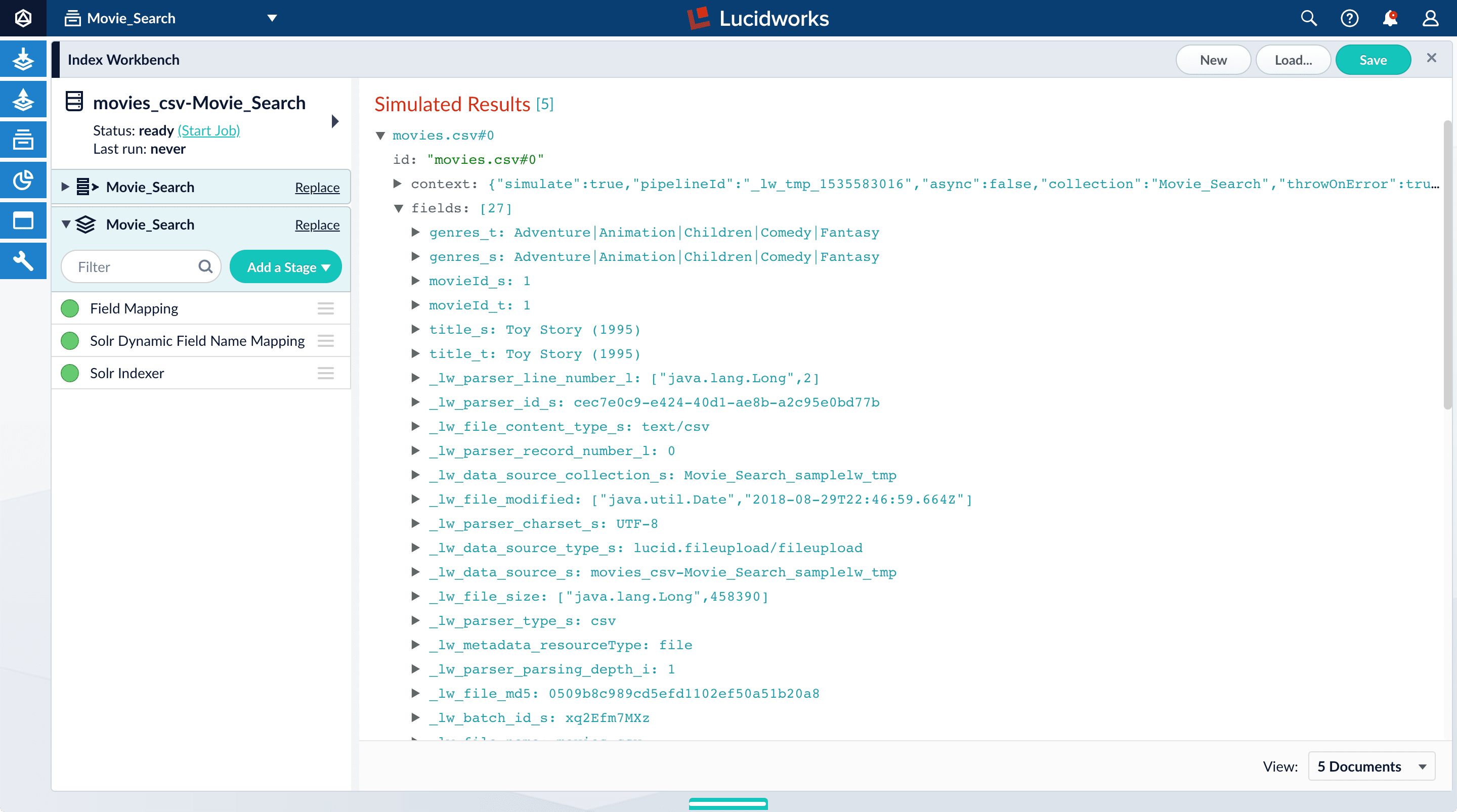
The View Documents field in the lower right lets you select the number of documents to preview.
Analyze the default output
-
Review the preview to inspect how Managed Fusion interpreted the original fields:
-
genresbecamegenres_t(thetext_generalfield type) andgenres_s(thestringfield type). String fields are useful for faceting and sorting, while text fields are for full-text search. At this point, Managed Fusion cannot determine whether you intend to use this field for faceting and sorting, for full-text search, or for both. -
Similarly,
titlebecametitle_tandtitle_sbecause Managed Fusion cannot determine whether you intend to use this field for faceting and sorting, for full-text search, or for both. -
Like the other fields,
movieIdbecamemovieId_tandmovieId_sbecause Managed Fusion cannot determine whether you intend to use this field for faceting and sorting, for full-text search, or for both. This might seem odd, because the original field contains numbers. But, at this stage, Managed Fusion createstext_generalandstringfields. To use the contents of this field as an integer, you would map the field to an integer field. -
Fields that begin with
_lwfields contain data that Managed Fusion creates for its own housekeeping. You can disregard these entries.
These fields are created by the Solr Dynamic Field Name Mapping stage in the default index pipeline. This stage attempts to automatically detect field types, and renames fields accordingly. For this tutorial, you will manually configure the fields instead.
-
-
Click the green circle next to the Solr Dynamic Field Name Mapping stage to turn off the stage.
Your data’s original fields display:
genres,movieId, andtitle.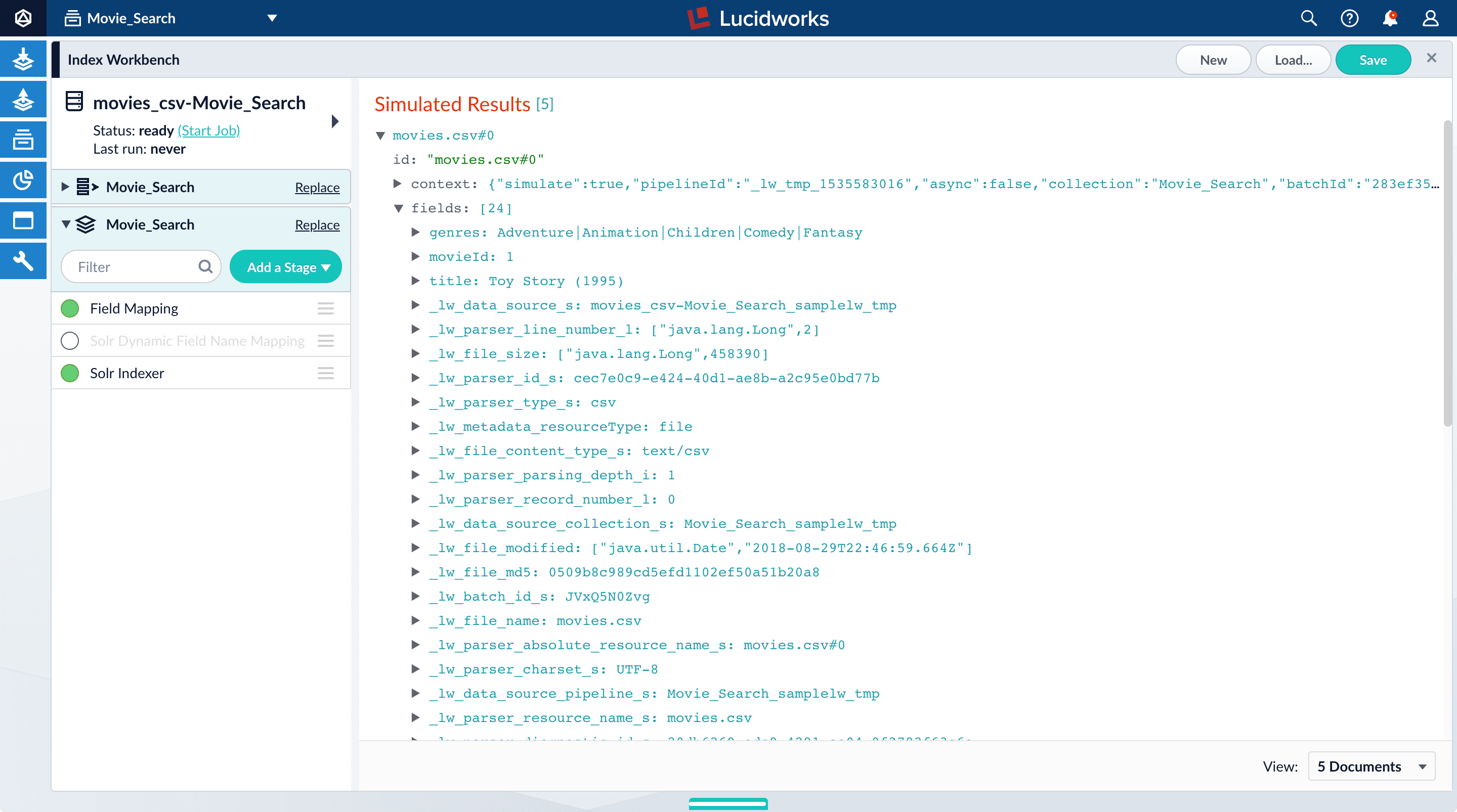
Configure the index pipeline
In this section, you will:
-
Configure the field mappings in the index pipeline so each field has the correct data type.
-
Split the
genresfield into multiple values so each value can be used as a facet in Part 3 - Query Data.
Configure field mappings
Field mappings control the data types of documents. Managed Fusion uses field name suffixes to determine field types. If the field name:
-
Contains a suffix, precise analysis and search occurs.
-
Does not contain a suffix, Managed Fusion stores the data as a string field and treats it as an unanalyzed whole.
This section provides examples of both instances.
-
In the list of index pipeline stages, click Field Mapping to open the Field Mapping stage configuration panel.
-
In Field Translations, click Add
 to create a new field mapping rule.
to create a new field mapping rule. -
In the Source Field, enter
genres. -
In the Target Field, enter
genres_ss.The field suffix
_ssmeans that this field is a multi-valued string field.Managed Fusion currently interprets this field as having a single value. The field actually contains a pipe-delimited array of values. When you finish configuring field mappings, subsequent steps will guide you to change the value type. -
In Operation, select move.
The move operation means that the resulting document contains
genres_ssinstead ofgenres.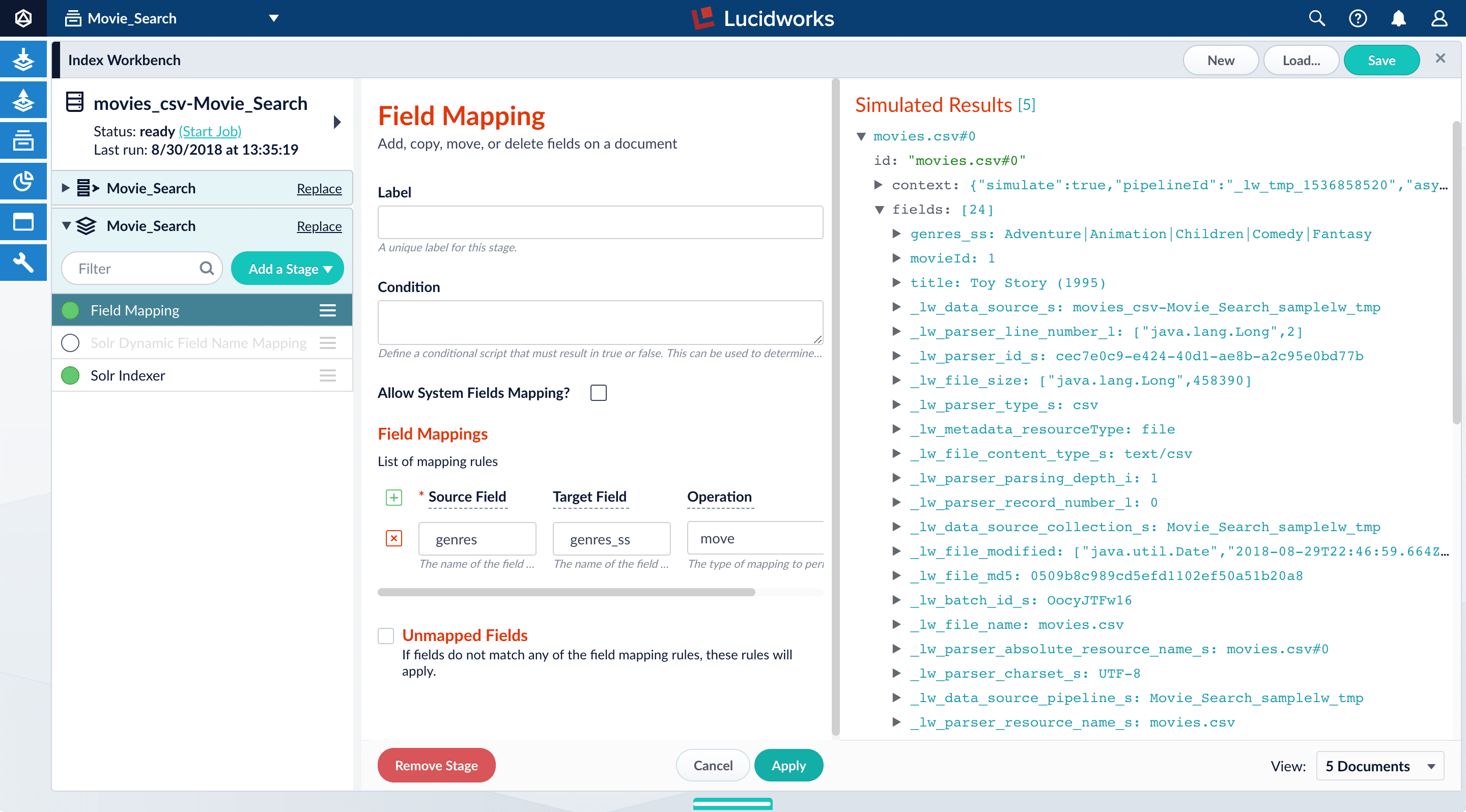
-
Click Apply. The new configuration runs the simulation again and updates the preview panel contents, changing the field name to
genres_ss.Before After 

-
Click Add
 to add more field mapping rules as follows:
to add more field mapping rules as follows:-
The
movieIdfield is a unique document identifier. Select to copy it into the document’sidfield. -
The
titleshould be searchable as a text field, so select to move it to thetitle_txtfield.The field mappings display as:
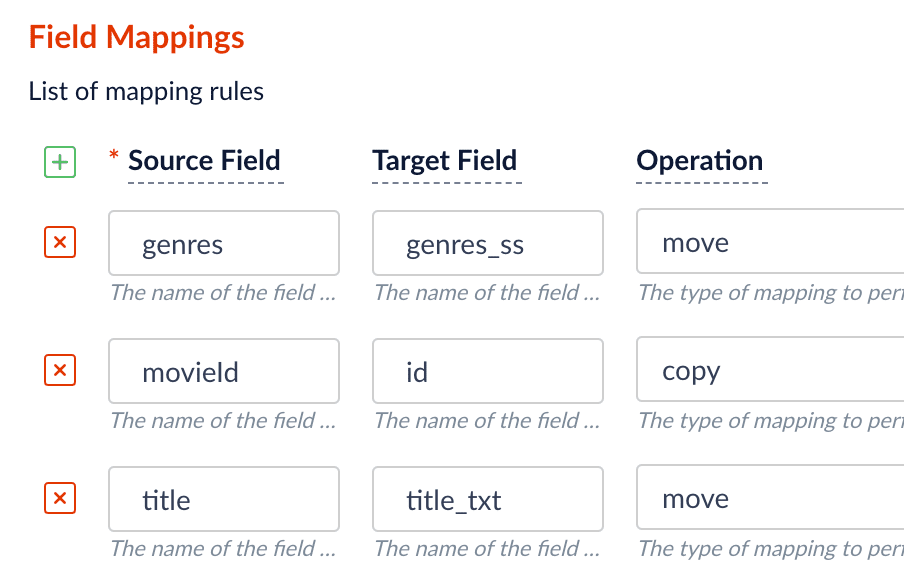
-
-
Click Apply. The results using those field mappings display in the preview panel.
Before After 

-
In the upper right, click Save. The changes to the index pipeline make the document ID more useful and the full text of the movie titles searchable.
| Because the input documents in this tutorial are simple documents with a fixed number of known fields, it is easy to configure the Field Mapping stage to ensure the correct document structure. When documents have large numbers of fields, the Solr Dynamic Field Mapping stage can reduce the work required to configure the index pipeline. |
Split a multivalue field
The genres_ss field has been parsed as a single value field, but it is really a pipe-delimited array of values. To split this field into its constituent values, add a Regex Field Extraction stage to your index pipeline. This stage uses regular expressions to extract data from specific fields. It can append or overwrite existing fields with the extracted data, or use the data to populate new fields.
-
Click Add a stage.
-
Scroll down to Field Transformation and select Regex Field Extraction.
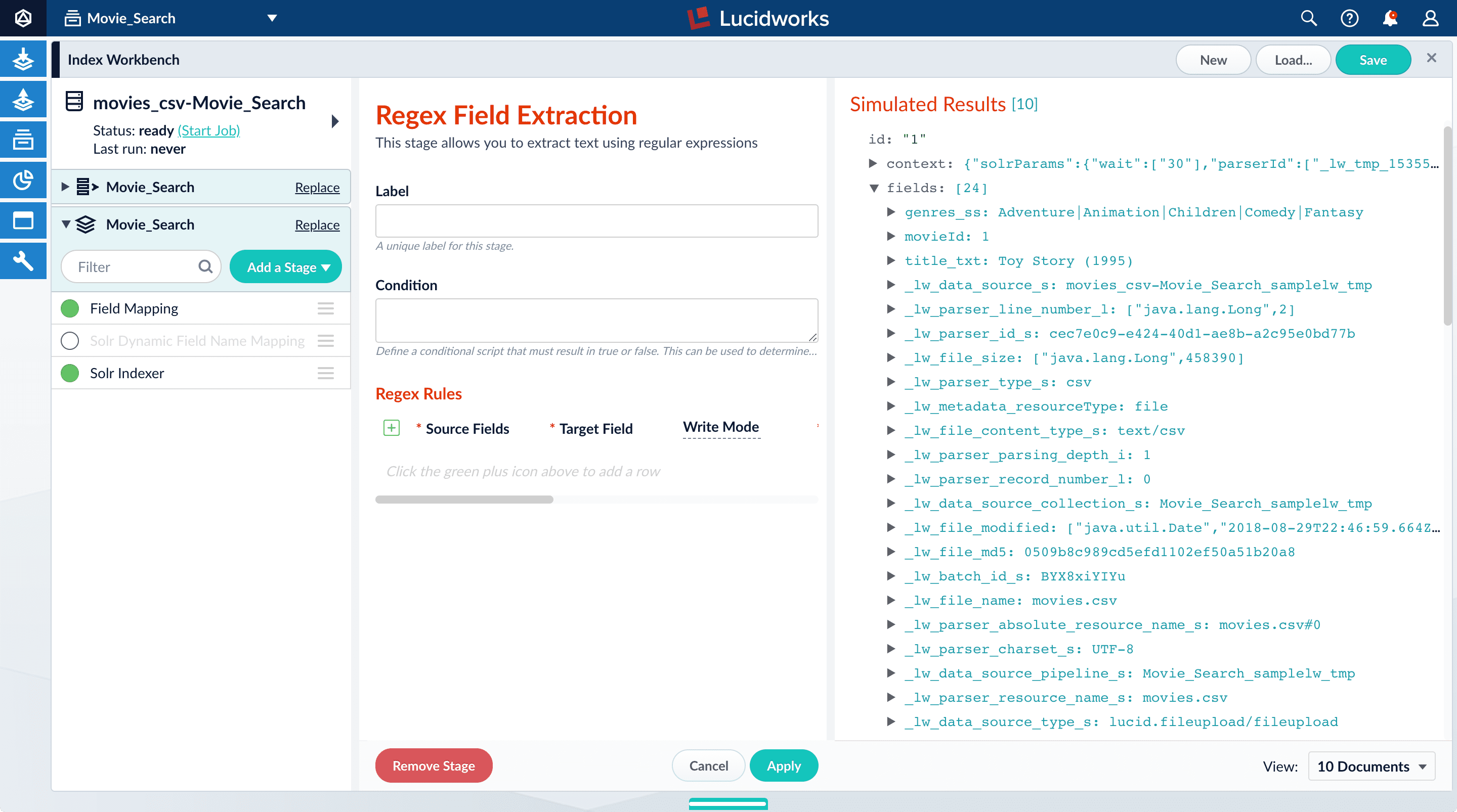
-
In Regex Rules, click Add
 .
. -
On the new line, hover over the
[…]under Source Fields, and click Edit .
. -
In the Source Fields screen, click Add
 .
. -
Enter
genres_ssand click Apply. -
In Target Field, enter
genres_ss. -
In the Write Mode field, select overwrite.
-
In the Regex Pattern field, paste this expression:
[^|\s][^\|]*[^|\s]*You might need to scroll horizontally to see this field on the screen. The first bracketed term in the regex matches any character that is not a vertical bar or a space. The second term matches any character that is not a vertical bar, zero or more times. The last term matches any character that is not a vertical bar, zero or more times.
-
In Return If No Match, select
input_string. -
Click Apply.
Initially, your data does not change.
-
In the list of index pipeline stages, click and drag the Regex Field Extraction stage so it processes after the Field Mapping stage:
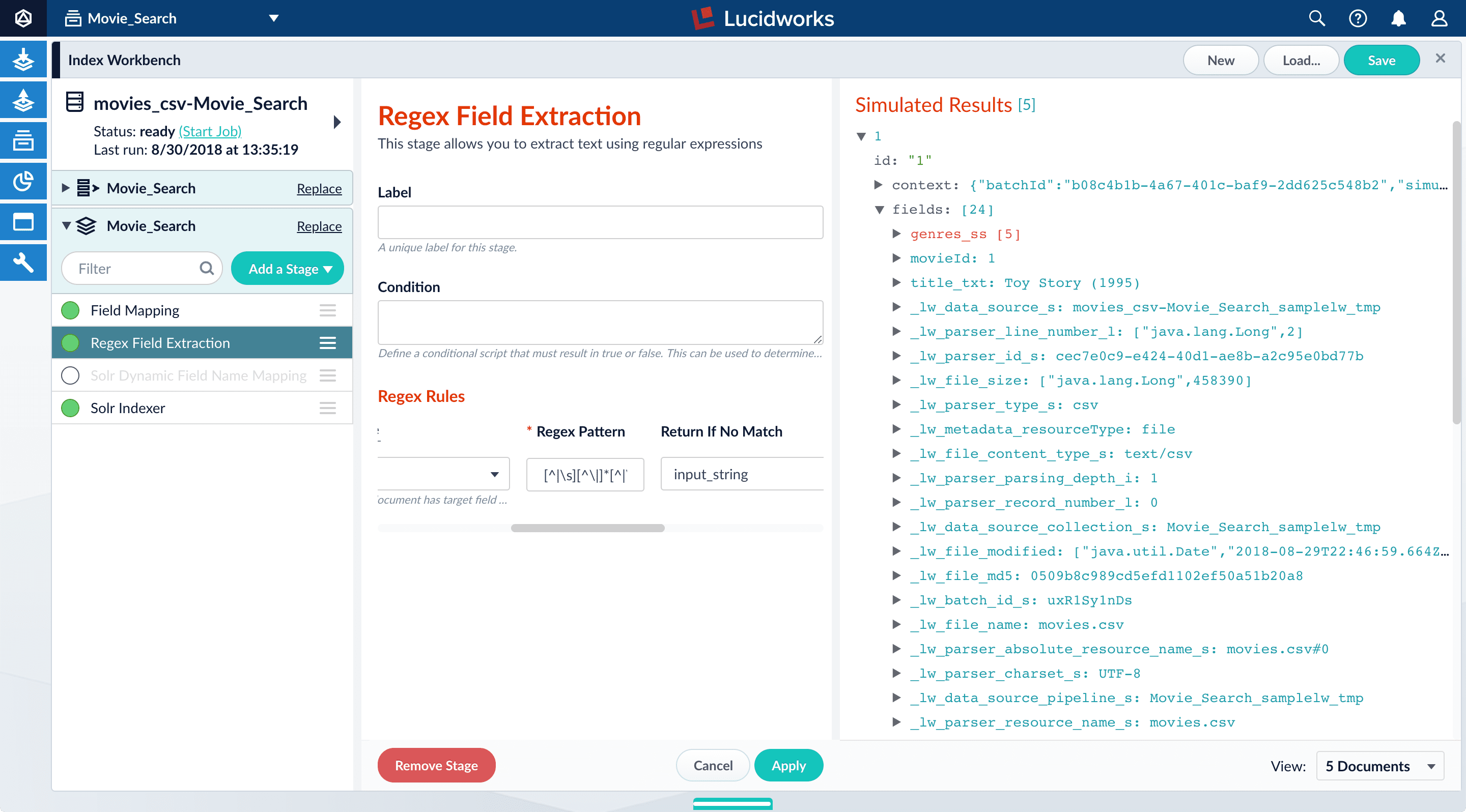
Now the preview shows multiple values for the
genres_ssfield:Before After 

If the preview panel does not update automatically, select a different number of documents to view using the dropdown in the bottom right of the screen. This forces the preview to update. -
To view the values of the
genres_ssfield, click the right triangle to expand it and
to expand it and valuesunder it:
These field values are useful for faceting, which is detailed in Part 3 - Query Data.
-
In the upper right, click Save to save the changes to the index pipeline.
Create a new field from part of an existing one
Currently, the title_txt field also contains the year in which the movie was released. To make the field more useful for faceting, the year needs to be a separate field. The Regex Field Extraction stage will separate the data.
-
In the list of index pipeline stages, click Regex Field Extraction.
-
In the Regex Field Extraction configuration panel, under Regex Rules, click Add
 .
. -
On the new line, hover over the
[…]under Source Fields, and then click Edit .
. -
In the Source Fields screen, click Add
 .
. -
Enter
title_txtand click Apply. -
In Target Field, enter
year_i.The
_isuffix indicates an integer point field (specifically, that the field is a dynamic field with a point integer,pint, field type). Managed Fusion creates this new field when the regular expression matches the contents of the source field.When you use the Regex Field Extraction stage to create a new field, the value of Write Mode does not affect the data. -
In the Regex Pattern field, paste this expression to match the digits inside the parentheses at the end of the
title_txtvalue:\(([0-9]+)\)$ -
In the Regex Capture Group field, enter
1. This lets the index pipeline stage transfer the year into theyear_ifield.Scroll to the right to see this field on the screen. -
Click Apply.
Now the preview includes the new
year_ifield:Before After 

-
In the upper right, click Save to save the changes to the index pipeline.
Trim a field’s value
The title_txt field still includes the year of the film’s release, which you have extracted into its own field, year_i. To refine the field for faceting, trim year_i from the title_txt values so only the title text remains.
-
In the list of index pipeline stages, click Regex Field Extraction.
-
In the Regex Field Extraction configuration panel, under Regex Rules, click Add
 .
. -
On the new line, hover over Source Fields and click Edit
 .
. -
In the Source Fields screen, click Add
 .
. -
Enter
title_txtand click Apply. -
In Target Field, enter
title_txt. -
In the Write Mode field, select
overwrite. -
In the Regex Pattern field, paste this expression to match the digits inside the parentheses at the end of the
title_txtvalue:^(.+)\s\(([0-9]+)\)$ -
In the Regex Capture Group field, enter
1. -
Click Apply.
The preview pane displays the
title_txtfield with only the title string:Before After 

-
In the upper right, click Save to save the changes to the index pipeline.
Run the datasource job
In the upper left, click Start job to index the data using the configured index pipeline.
This launches a datasource job that imports and indexes the complete contents of your movies.csv file using the configuration you just saved.
Your datasource job is finished when the Index Workbench displays Status: success in the upper left. If the status does not change, click to return to the launcher and relaunch your app to refresh the status.
Close panels you no longer need open
If you do not manually close each panel, Managed Fusion opens panels beside already open panels. Click Close ![]() to close all of the open panels.
to close all of the open panels.
Reindex the datasource
Documents are associated with a collection through the name of the datasource, which is stored as a value in the _lw_data_source_s field.
For various reasons, you may wish to remove all documents associated with a datasource from a collection before using CrawlDB to add relevant documents back to the collection. This process is known as reindexing.
-
Navigate to Indexing
 > Datasources.
> Datasources. -
Select the datasource name.
-
Click Clear Datasource. This removes all documents with the selected datasource name in the
_lw_data_source_sfield. -
When the documents are removed, repeat the steps in Configure the index pipeline to reindex the data.
| Do not use the name of an existing datasource if you change the name of a datasource or if you create a new datasource. If an identical name is used, all document associations will be shared between the datasource names. |
Summary
The parts of this tutorial so far have guided you to:
-
Move 9,125 movie listings from the MovieLens database into Managed Fusion
-
Customize the data type for each field
-
Split multivalued fields to treat its values individually
-
Create a new field that contains partial contents of a different field
-
Trimmed the content of the original multivalue field
The example displays the initial index versus the results after the field mappings and extractions:
| Before | After |
|---|---|
|
|
Next steps
In Part 3 - Query Data, you will use Query Workbench to get search results from your collection and configure the query pipeline that customizes those results. You will also add faceting using the genres_ss and year_i fields so users can easily filter their search results.
Additional resources
|
Lucidworks offers free training to help you get started. The Course for Indexing Data focuses on how to ingest and store your data in a format that’s optimized for search: Visit the LucidAcademy to see the full training catalog. |

